Major Export Products
- Home Major Export Product
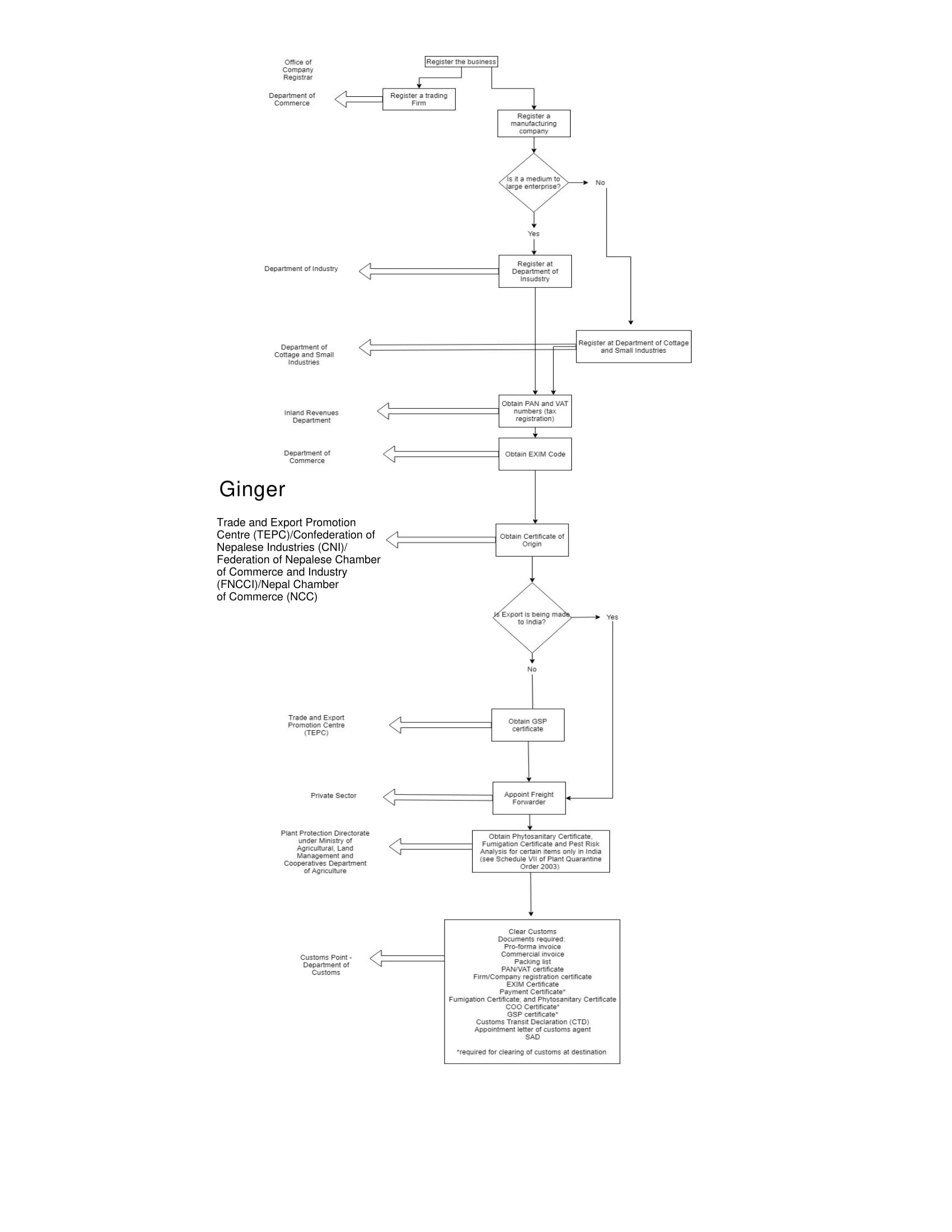
Ginger
Ginger is one of the most popular spices in the world. The ever popular rhizome is native to South and Southeast Asia and is widely used in kitchens all over the world owing to its taste and medicinal properties. In the South Asian subcontinent, it is used as an anti-inflammatory agent although there are studies that document its uses in cold and flu prevention and treatment, morning sickness and even in cancer treatment.
Ginger’s most well-known medicinal use is as a digestive-aid, to relieve tummy pain, nausea and diarrhoea, as well as morning sickness and travel sickness. This is thought to be because of high levels of gingerol; a powerful component that gives it its natural zingy flavour, and which acts as an anti-inflammatory in the body. The anti-inflammatory properties of ginger are thought to provide pain relief in a number of ways, from halting migraines, to easing the aches of arthritis.
Studies have started showing exciting results on the effect ginger on ovarian cancer: Although more research is needed, it seems that ginger has the ability to eliminate the cancerous ovarian cells. It also seems to dramatically slow the progress of bowel cancer. Spoon feeding of ginger ale is also practiced on the children when they have flu. Ginger also helps in boosting the immune system.
Nepal is the third largest producer of ginger in the world. Ginger from Nepal are known to be organic and are found to be of high quality in terms of oil content and low fibre. Ginger from Nepal is primarily exported to India although some exporters are marketing their products in Japan and Arabian Peninsula. Even United States, United Kingdom and Australia buy ginger from Nepal.
Production:
In total, Nepal produces more than 250,000 MT of ginger of which more than 50 per cent of total output is exported. It is assumed that around 200,000 families are engaged in production of ginger throughout Nepal.
Geographical presence
Ginger is produced in more than 65 districts all over Nepal. Doti, Kailali, Surkhet, and Salyan in western Nepal; Palpa, Syangja, and Nawalparasi in Central Nepal; and Ilam, Jhapa and Sindhupalchowk in Eastern Nepal, are some of the major ginger producing districts in the country.
Non-tariff specifications
India is the largest importer of ginger from Nepal and its Food Safety and Standards (Food Products Standards and Food Additives) Regulations, 2011 dictates standard for ginger, specially dried ginger and ginger powder.
Specification of Dried ginger in India:
| Characteristics | Requirement (India) | Requirement (Nepal) | |
| Extraneous matter | Not more than 1% by weight | Not exceeding 2% | |
| Moisture | Not more than 12% by weight | - | |
| Total ash on dry basis | Unbleached | Not more than 8% by weight | - |
| Bleached | Not more than 12% by weight | - | |
| Calcium as Calcium oxide on dry basis | Unbleached | Not more than 1.1% by weight | Not more than 4% by weight |
| Bleached | Not more than 2.5% by weight | Not more than 4% by weight | |
| Volatile oil content on dry basis | Not less than 1.5% by v/w | Not less than 1% by v/w | |
| Insect Damaged matter | Not more than 1.0 percent by weight | - | |
(Source: Food Safety and Standards (Food Products Standards and Food Additives) Regulations, 2011)
Specification of Dried ginger (powder) in India
| Characteristics | Requirement (India) | Requirement (Nepal) | |
| Moisture | Not more than 12% by weight | Not exceeding 13% by weight | |
| Total ash on dry basis | Unbleached | Not more than 8% by weight | Not exceeding 10% by weight |
| Bleached | Not more than 12% by weight | Not exceeding 10% by weight | |
| Calcium as Calcium oxide on dry basis | Unbleached | Not more than 1.1% by weight | Not exceeding 4% by weight |
| Bleached | Not more than 2.5% by weight | Not exceeding 4% by weight | |
| Volatile oil content on dry basis | Not less than 1.5% by v/w | Not less than 1.% by v/w | |
| Water soluble ash on dry basis | Not less than 1.7% by weight | - | |
| Acid insoluble ash on dry basis | Not more than 1.0% by weight | Not exceeding 1% by weight | |
| Alcohol (90% v/w) soluble extract on dry basis | Not less than 5.1% by weight | Not less than 4.5% by weight | |
| Cold water-soluble extract on dry basis | Not less than 11.4% by weight | Not less than 1% by weight | |
(Source: Food Safety and Standards (Food Products Standards and Food Additives) Regulations, 2011)
Limit of radiation level in dried ginger in India
| Dose of irradiation (kGy) | Minimum | Maximum | Overall Average |
| Ginger | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.09 |
(Source: Prevention of Food Adulteration Act 1955)
Maximum permitted limit of certain additives in India
| Additives | Limit |
| Ascorbyl Esters | 500 mg/kg |
| Acesulfame K | 2000 mg/kg |
| Butylated hydroxyanisole | 200 mg/kg |
| Butylated hydroxytoluene | 200 mg/kg |
| Ethylene Diamine Tetra Acetates | 70 mg/kg |
| Neotame | 32 mg/kg |
| Propyl Gallate | 200 mg/kg |
| Sorbates | 1000 mg/kg |
| Tertiary Butyl Hydroquinone | 200 mg/kg |
| Polysorbates | 2000 mg/kg |
| Sulfites | 150 mg/kg |
(Source: Food Safety and Standards (Food Products Standards and Food Additives) Regulations, 2011)
To find out information on country-specific tariff rates, check International Trade Centre’s MAcMAp. Put Nepal in exporting country field and select the destination country, exporting commodity and year to be exported to find the tariff rate. To find country-specific non-tariff requirements click here.
Trade Statistics
Related Trader
No trader Found
Related Measures and Procedures
Measures
| Name | Type | Agency | Description | Comments | Law | Validity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Certificate of Origin | Formality Requirement | Ministry of Finance | Section 21. Attachment of the documents with the declaration form: (1) A person importing or exporting goods pursuant to Section 18 of the Act, while submitting declaration form to the customs officer, shall submit the following documents including Certificate of Origin. | Comments | Customs Regulation, 2064 (2007) | 9999-12-31 00:00:00.0 |
| Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) | Certificate Requirement | Ministry of Finance | 21. Attachment of the documents with the declaration form:(1) As per section 18 of the Act, the person importing or exporting goods,while submitting declaration form to the customs officer, should submitfollowing documents(a)..(b)...(c) For exportation(1) Invoice(2) Packing list(3) Certificate of Origin(4) Banking document regarding payment procedure, in case of export to third country(5) Documents which are required as per prevailing law regarding the recommendation, license, or certificate from any institution. However Certificate of Origin shall not be mandatory for the export in which G.S.P. certificate is required. | Comments | Customs Regulation, 2064 (2007) | 9999-12-31 00:00:00.0 |
Procedures
| Name | Description | Category | View Procedure Detail with Relevant Forms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Certificate of Origin | Procedure to apply for Certificate of Origin | Procedure | View |
Product Workflow